A blood clot is the most common cause of a blocked coronary artery. Usually, the artery is already partially narrowed by atheromas. An atheroma may rupture or tear, narrowing the artery further and making blockage by a clot more likely.
The ruptured atheroma not only reduces the flow of blood through an artery but also releases substances that make platelets stickier, further encouraging clots to form.
Uncommonly, a heart attack results when a clot forms in the heart itself, breaks away, and lodges in a coronary artery. Another uncommon cause is a spasm of a coronary artery that stops blood flow. Spasms may be caused by drugs. Sometimes the cause is unknown.
Heart Attack: Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Signs and Symptoms
present as pain that is crushing, tightness, squeezing, band-like, radiating, cyanosis, sweating, cold, “clenching fist over heart”, pain in the ear, umbilicus, jaw, teeth, back, arm, hand pain (often on the ulnar side), autonomic response of vomiting, nausea or a feeling of impending doom.
About one third of people who have a heart attack do not have chest pain. Such people are more likely to be women, people who are not white, those who are older than 75, those who have heart failure or diabetes, or those who have had a stroke.
Other symptoms include a feeling of faintness, sudden heavy sweating, nausea, shortness of breath, and a heavy pounding of the heart.
Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) occur in more than 90% of people who have had a heart attack. Immediately and up to a few days after a heart attack, abnormal heart rhythms are a common reason that the heart cannot pump adequately.
Abnormal heart rhythms originating in the ventricles (ventricular arrhythmias) may greatly interfere with the heart’s pumping ability or may cause the heart to stop pumping effectively (cardiac arrest). A loss of consciousness or death can result. Sometimes loss of consciousness is the first symptom of a heart attack.
If you suspect a heart attack, seek emergency medical treatment immediately. Should a heart attack occur, you should go to the emergency room and seek help immediately. Time is of essence. Only examination by a doctor, who will administer an electrocardiogram (EKG) and/or a blood test, can confirm if you are having a heart attack.
The most important thing to do if you think you are having heart attack symptoms:
Dial 911 to call an ambulance or get to a hospital emergency room as quickly as possible so the doctor can examine and treat you.
Crush or chew a full-strength aspirin (swallow with a glass of water) to prevent further blood clotting.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is a combination of rescue breathing and chest compressions delivered to victims thought to be in cardiac arrest. When cardiac arrest occurs, the heart stops pumping blood. CPR can support a small amount of blood flow to the heart and brain to “buy time” until normal heart function is restored.
To learn CPR properly, take an accredited first-aid training course, including CPR and how to use an automatic external defibrillator (AED).
Before you begin, assess the situation before starting CPR:
- Is the person conscious or unconscious?
Remember the ABCs
Think ABC
— Airway, Breathing and Circulation — to remember the steps explained below. Move quickly through Airway and Breathing to begin chest compressions.
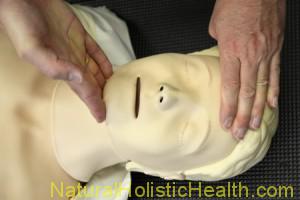
AIRWAY
: Clear the airway

BREATHING
: Breathe for the person

CIRCULATION
: Restore blood circulation with chest compressions
The American Heart Association recommends administering one shock, then resuming CPR — starting with chest compressions — for two more minutes before administering a second shock.
If you’re not trained to use an AED, a 911 operator may be able to guide you in its use. Trained staff at many public places are also able to provide and use an AED.
Continue CPR until there are signs of movement or until emergency medical personnel take over.
Keep Your Heart Healthy!
Cardio Support
contains ingredients that affect different aspects of cardiovascular health, including arterial integrity, blood health, heart muscle strength and better blood flow.
Additionally, the ingredients in
Cardio Support
overlap their abilities, to enhance one another’s effects, increasing long-term heart health and protection against degenerative disease.
Cardio Support
is the only natural supplement that we are aware of which utilizes enteric coating technology to safely release the active ingredients in the stomach.
This delivery method not only protects the enzymes such as Nattokinase but also greatly enhances the efficacy of other ingredients present such as Resveratrol and L-Glutathione.
No other formula covers so many ‘angles’ to manage and protect your cardiovascular system, and yet Cardio Support is still natural with no known side effects.
Learn more about
Cardio Support
now.
